-
+
-
Food
+
Food
-
Feeding
+
Feeding
Brands in Catagory
-
Health
+
Health
Brands in Catagory
-
Outing
+
Outing
Brands in Catagory
-
Home
+
Home
Brands in Catagory
-
Sleeping
+
Sleeping
Brands in Catagory
-
Education
+
Education
Brands in Catagory
-
Book / CD
+
Book / CD
Brands in Catagory
-
Playing
+
Playing
Brands in Catagory
-
Wearing
+
Wearing
Brands in Catagory
-
Cartoon Characters
+
Cartoon Characters
Brands in Catagory
-
Jellycat Station
+
Jellycat Station
-
Gifts
+
-
My Pets
+
-
Clearance
- Swim Wear Clearance
- Sleeping Clearance
- Carseat Clearance
- Wall Decorations
- Baby Carrier Clearance
- Feeding Clearance
- Stroller Clearance
- Clothing Clearance
- Book Clearance
- Bathing/Toilet
- Clearance Toys
- Bag / Luggage
- Books/CDs
- Electronic / Electric Item
- Aprica
- B&H
- Babisil
- Baby-Nova
- BabyFEHN
- Babymate
- Bambino Mio
- Barron's
- BEABA
- Belly Bandit
- Benbat
- Bibetta
- Bloom
- Bravado
- California Bear
- Charlie Banana
- Clementoni
- Cuski
- Cybex
- Diono
- Ecomom
- Egmont
- Ergobaby
- Grubby Bubby
- GUND
- I-Angel
- iPlay
- Itzy Ritzy
- Ju-Ju-Be
- Kee-Ka
- Koolsun
- Krooom
- Label Label
- Lascal
- LÍLLÉBaby
- Lisciani
- LittleLife
- Love To Dream
- Lucky Baby
- Medela
- Melissa & Doug
- Moo Moo Kow
- Mum2Mum
- Others
- OXO
- Peaceable Kingdom
- Peacock
- PearHead
- Pediped
- Petite Creations
- Philips Avent
- Plage
- Playtex
- Precidio
- Scholastic
- Skip*Hop
- The Cuties and Pal
- Thermos
- Tiny Love
- Tommee Tippee
- TotSeat
- Trunki
- Tum Tum
- Twin Sisters
- Under the Nile
- Usborne
- Vulli
- Zoli
Clearance Brands:
Joint OK+ Collagen Peptides (Tendon-Bone PCP) - 11.7g x 15 sachets - JointOK
Free Local Delivery (HK) for Orders over HK300
Extra 2% Off - Payment by FPS (HK)
Quantity Discount
| Ordered Quantity | Price Per Unit |
| 10 or more | HK$ 500 |
| Discount: | 21% (-HK$ 130) |
Love+ Joint OK+ Patented Collagen Peptides - Tendon-Bone PCP Powder
Make things possible, easy and work for quality life.
Strong Bones & Physical Strength
- Good for bones, tendons & ligaments
- Improve bone mass density, reduce risk of bone breaking and falling in frail
- Improve control, stability and sports performance
- Improve flexibility, reduce injuries, accelerate return-to-play or work
- Country of Origin: Germany
- Net Weight: 11.7g x 15 sachets
- Ingredients: Tendon-Bone Collagen Peptides (Powder), Calcium, Magnesium, Vitamin D
- Easily absorbed >95% (Oesser 1999)
Direction:
1 sachet (10 grams) a day, mixed by stirring in water, beverages such as soup, soy milk, milk, tea or coffee, etc., or foods such as porridge, oats, yoghurt, congee, etc.
(Temperature below 50 ° C)
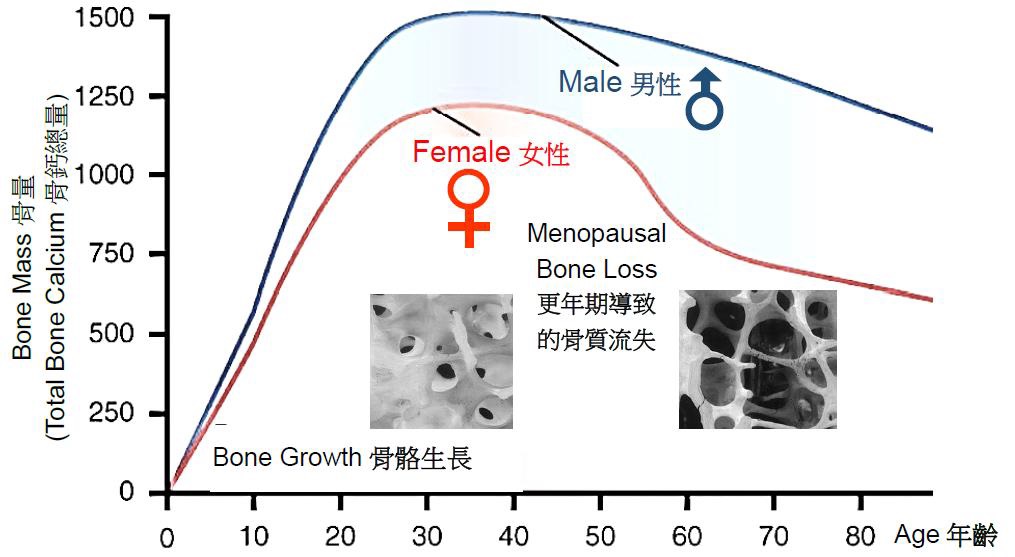
1) Is bone mass density (BMD) related to age?
Bone mass grows and peaks at age about 30, then begins to lose
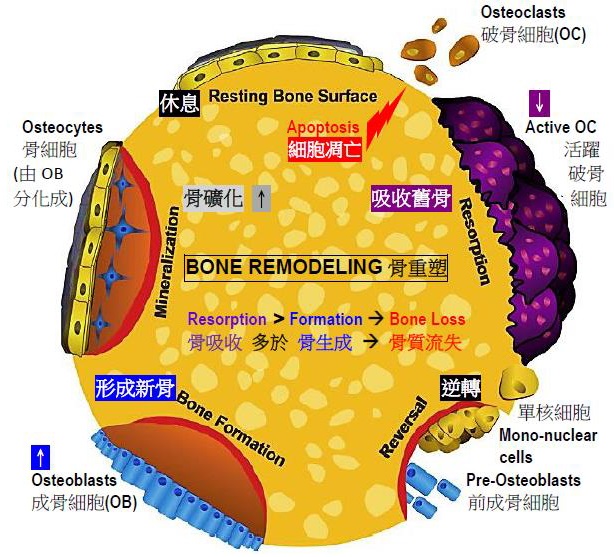
2) What is Bone Remodeling?
Bone is constantly in a cycle of being broken down and reformed (Bone Remodeling).
Bone is made up of living cells reabsorb bone while osteoblasts build new bone, the bone mass is stabilized if these cell activities are balanced
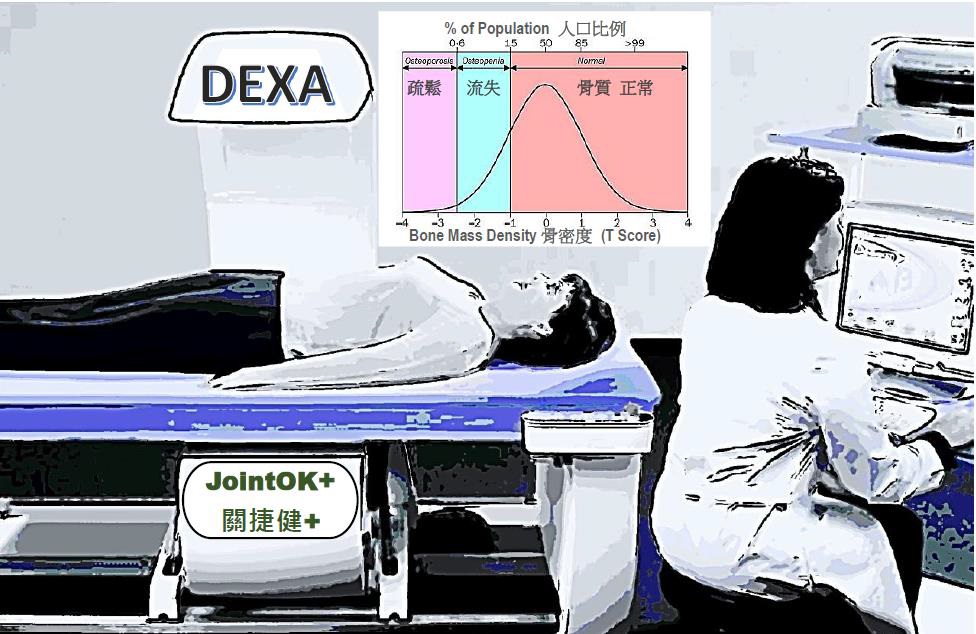
3) What are Bone density scan (DEXA scan) and T-score?
DEXA (Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry) is used to measure the bone density. Your bone density is measured and compared to that of a healthy young adult. The difference is calculated as a standard deviation (SD) called a T score.
- T-score above -1 SD is normal
- T score between -1 and -2.5 SD is regarded as osteopenia
- T score below -2.5 is defined as osteoporosis
4) What is Osteopenia?
Bone is composed of living cells. Due to aging and less hormone, the rate of bone degradation is faster than rebuilding, resulting in loss of bone mass.
Osteopenia (bone loss before osteoporosis, -2.5 < T-score < -1.0) is when your bone density is lower than the average of same age, but not as low as osteoporosis.
5) What is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis (T-score <-2.5) is a metabolic disease of bone, the reduction in bone density and quality makes bones weak and susceptibility to fracture.
Osteoporosis has no symptoms, it is usually not painful until a bone is broken. The characteristic stooped (bent forward) posture will happen if the spinal bones are broken.
About 1 in 3 women and 1 in 5 men aged over 50 suffered from osteoporosis.
6) What are the causes of osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis will result if bone loss is faster than normal and the risk of broken bones will increase.
In women aged over 40 or menopausal women, estrogen secretion drops or stops, osteoclasts become more active than osteoblasts and bone loss increases, bones become more fragile and risk of osteoporotic fractures increases.
The risk factors are:
- Women deficient in estrogen or after ovariectomy
- Long-term use of steroid medicines (asthma, breast and prostate cancer patients)
- Hormone-related conditions such as hyperthyroidism, Cushing's syndrome (hypercortisolism)
- Inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis
- Malabsorption or eating disorders (such as anorexia or binge eating disorder)
- Kidney or intestine problems affect vitamin D deficiency
- Partial eclipse or dieting (lack of calcium, vitamin D and collagen)
- Family history of bone problems
- Underweight (low body mass index BMI) or small body frame
- Lttle or no of exercise
- Heavy drinking and smoking, excessive caffeinated drinks
- Excess sodium (salt) intake
- After COVID-19
7) No bone pain means no osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis has no obvious signs and symptoms, so no bone pain does not mean that you do not suffer from osteoporosis. If you feel pain after a fall, it may be due to a broken bone.
8) Why is osteoporosis a "silent killer"?
Osteoporosis has no obvious symptoms easily to be neglected. If you have osteoporosis, falls are prone to bone fractures, commonly in wrist, lumbar spine and hip (Fig. 4). Gradual collapse of the spine will result in "hunchback".
Despite advance in medicine, the mortality rate of bone fractures in the elderly is as high as 20%, and half of the patients have less mobility affecting normal live. If the patient also has chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes, surgery may not be feasible or safe, other complications such as pneumonia and other diseases are prone to occur.
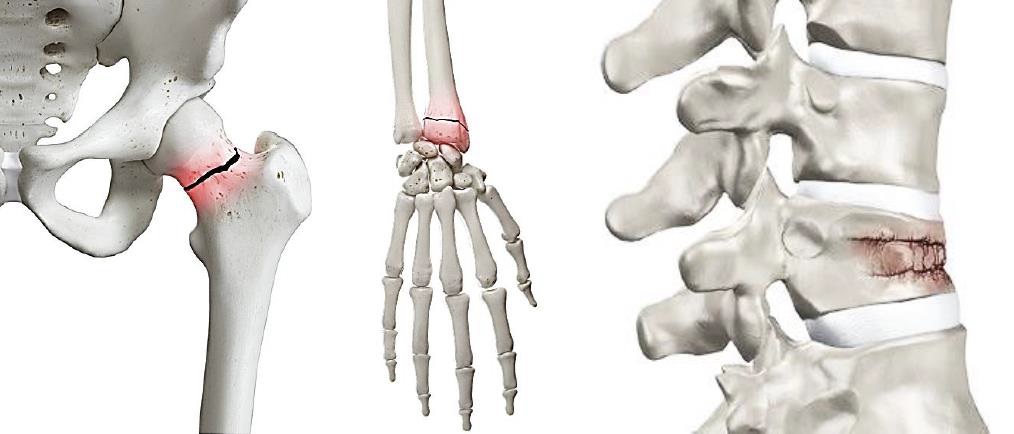
https://www.oshk.org.hk/uploads/files/2020/newspaper-4.pdf
9) How to prevent osteoporosis
To prevent osteoporosis, a healthy lifestyle should be adopted. During childhood and adolescence, take a balanced diet with food rich in calcium and vitamin D, moderate exposures to sunlight and do regular weight-bearing exercises to build strong healthy bones.
Maintaining an optimal body weight (BMI 18 – 23), avoid smoking or excessive alcoholic, reduce consumption of caffeinated drinks like tea or coffee, take measures to minimise the chance of fall-induced fractures.
In case of osteoporosis, bone loss can be slowed down bone density can be increased or by taking drugs or JointOK+關捷健+.
10) What is the importance of calcium to the body?
Calcium is the major inorganic component of bone, it contributes to bone rigidity, plays roles in nerve transmission, muscle contraction and blood clotting.
Adults should take not less than 1000mg calcium per day (H.K. Centre For Food Safety) (https://www.cfs.gov.hk/english/nutrient/nutrient.php )
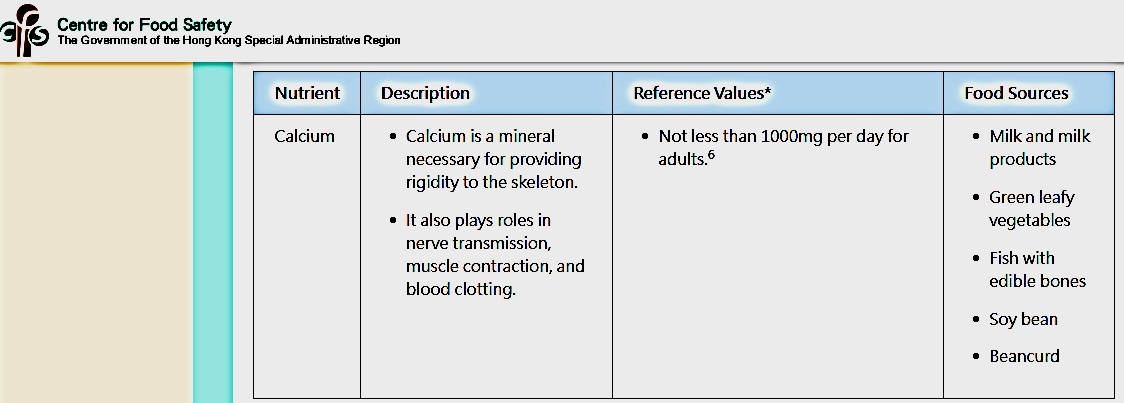
11) What food is rich in calcium?
Milk and milk products, green leafy vegetables (broccoli, choy sum), nuts, fish with edible bones like sardines, dried whitebait and dried shrimp, and calcium-fortified foods such as beancurd (tofu) are rich in calcium.
If you have lactose intolerance, allergy to nuts or crustaceans, you can take JointOK+關捷健+.
12) Can bone broth and pig trotter with vinegar strengthen bones?
13) Can high-calcium milk food treat osteoporosis?
Eating high-calcium foods such as high-calcium milk is not enough to treat osteoporosis. Firstly: calcium absorption needs vitamin D. Secondly: researches showed that even taking calcium and vitamin D together is not enough for the protection of osteoporotic patients. Orthopedics suggest using drugs that can inhibit osteoclasts or increase mineralization.
Net loss of bone mass after daily intake of 500 mg Calcium and 400 IU Vitamin D for 3 months.
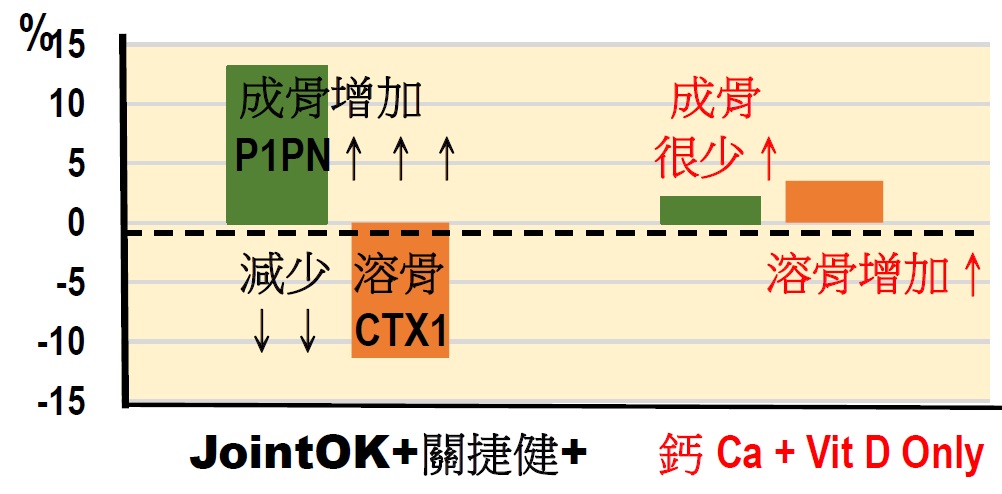
14) Is taking calcium and Vitamin D sufficient to prevent bone loss?
Some studies said yes while some said no, evidence that calcium supplements can prevent or manage osteoporosis may not be sufficient.
A review of 59 studies found that increasing calcium intake resulted in small but not clinically meaningful improvements in bone mass density (BMJ 2015; 351:h4183).
Another review of 33 studies found that calcium alone or in combination with vitamin D did not reduce risk of fractures in the elderly (JAMA. 2017 Dec 26;318(24):2466-2482).
15) How JointOK+ helps reduce bone loss and increase bone mass density?
Bones need not just Ca, Mg, vitamin D, but JointOK+ PCP (Molecules 2013, JAFC 2010) JointOK+ is a non-drug innovative bone supplement which differs from other collagen peptides in origin & composition, as well as bioavailability & mode of action. JointOK+ has triple actions against bone loss:
(1) Inhibit Osteoclasts (2) Stimulate Osteoblasts (3) Increase mineralization (Nutrients 2018, JBM2021, JMNI 2020)
(1) Inhibit Osteoclasts
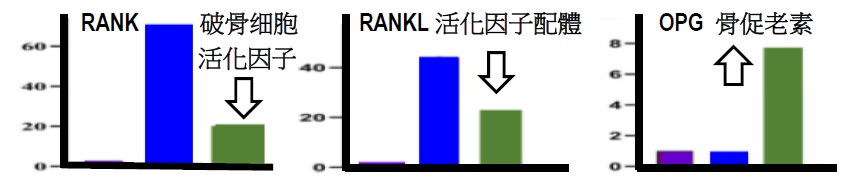
(2) Stimulate Osteoblasts
JointOK+ stimulate Osteoblasts to synthesize bone collagen matrix (collagen and osteocalcin)
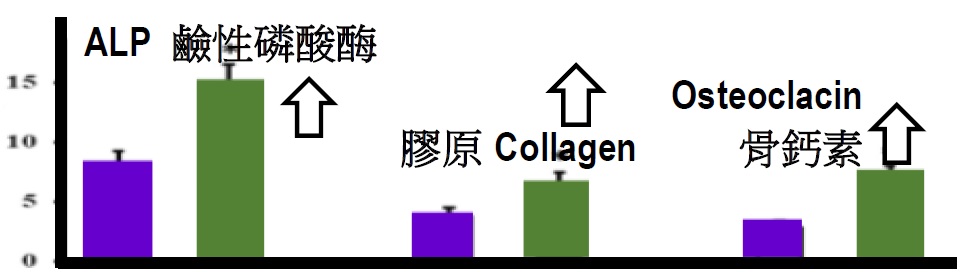
(3) Increase mineralization (J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020)
JointOK + activates alkaline phosphatase (ALP), enhance bone mineralization and increase bone mass

16) Why JointOK calcium is in the form of calcium carbonate?
Calcium carbonate is the most concentrated form of calcium, calcium carbonate provides more elemental calcium than many other calcium salts:
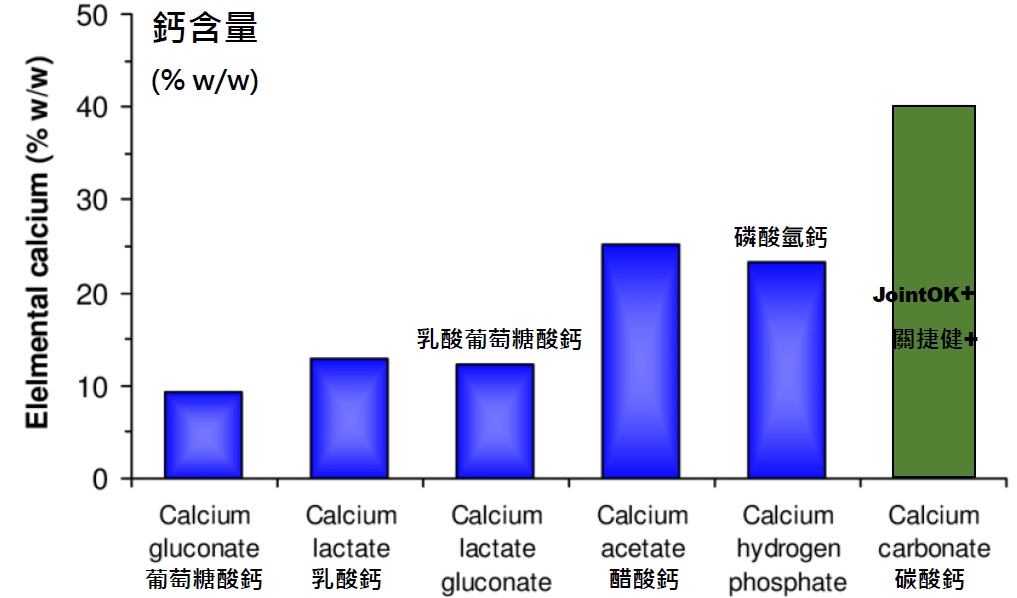
Silpakorn U Science & Tech J Vol.4(1), 2010
17) Why JointOK should be taken with food?
JointOK contains calcium carbonate which is better absorbed after meal.
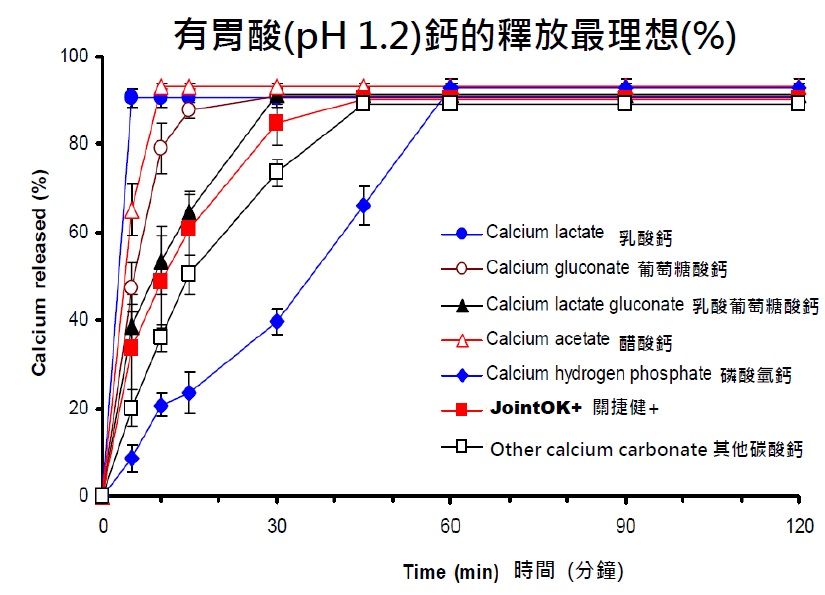
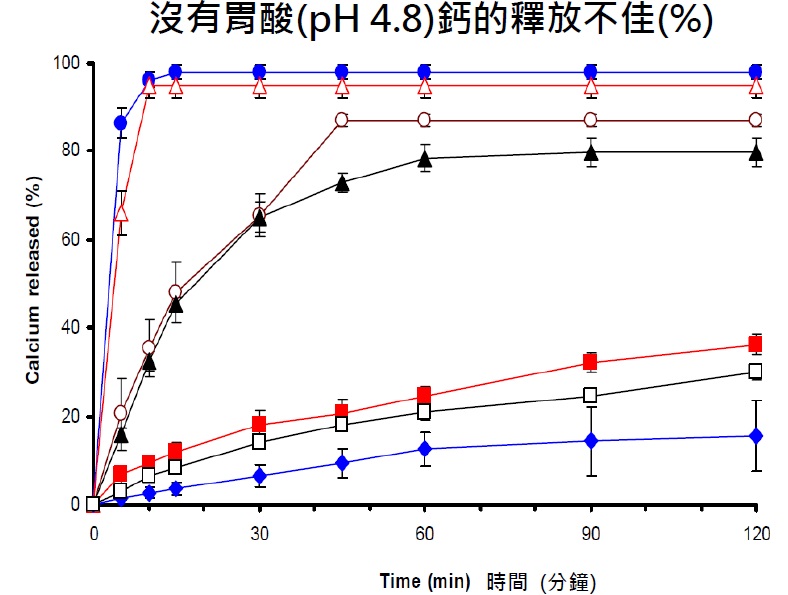
Silpakorn U Science & Tech J Vol.4(1), 2010
18) What may happen if too much calcium intake?
Too much calcium may cause hypercalcemia, kidney stones, digestive or heart problem. JointOK+ formula is based on clinical research, it contains 500mg calcium which is about 50% of daily requirement.
19) Why JointOK+ contains Vitamin D?
Vitamin D plays a key role in calcium absorption and helps regulate bone turnover.
USA National Institutes of Health (NIH) suggests taking 600 IU per day. Vitamin D can be obtained through sunlight exposure. (https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional/ )
JointOK+ formula (Tendon-Bone Proprietary Collagen Peptides + Calcium + Vitamin D + Magnesium) is based on its clinical study in Europe (ref: J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2020; 20(1):12-17)
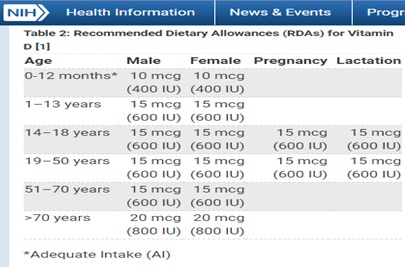
21) Why JointOK+ contains Magnesium?
Magnesium is essential and is involved in over 300 body biochemical reactions. Magnesium has roles in protein synthesis, enzyme action, muscular contraction and nerve transmission. About 60% of body magnesium is found in bones.
Hong Kong Centre For Food Safety suggests intake of magnesium per day not less than 220mg for women and 260mg for men.
JointOK+ formula also contains magnesium because a prospective observational cohort of over 48 000 postmenopausal women in Shanghai found that a 40–50 % reduction of osteoporotic risk only when a daily dietary Ca/Mg ratio is equal to or above 1⋅7.(Journal of Nutritional Science (2022), vol. 11, e62)
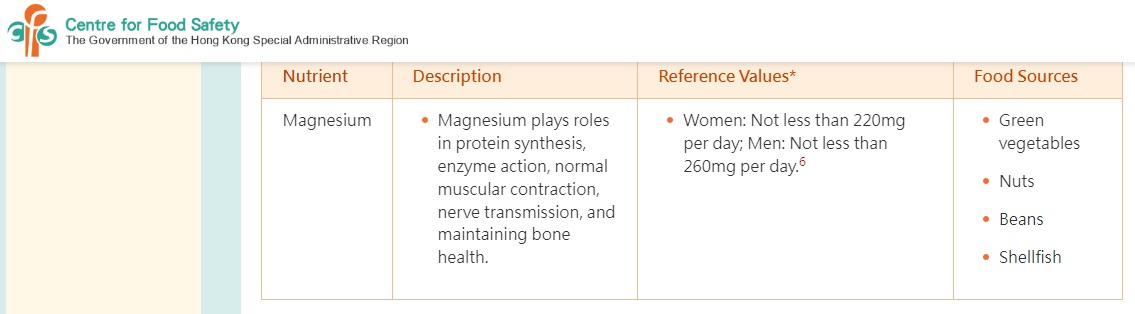
22) Who should take JointOK+?
- People with or at risk of bone loss:
- Adolescents need to strengthen bone tissues and structure
- Women deficient in estrogen or after ovariectomy
- Long-term use of steroid medicines (asthma, breast and prostate cancer patients)
- Hormone-related conditions such as hyperthyroidism, Cushing's syndrome (hypercortisolism)
- Inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis
- Malabsorption or eating disorders (such as anorexia or binge eating disorder)
- Kidney or intestine problems affect vitamin D deficiency
- Partial eclipse or dieting (lack of calcium, vitamin D and collagen)
- Family history of bone problems
- Underweight (low body mass index BMI) or small body frame
- Lttle or no of exercise
- Heavy drinking and smoking, excessive caffeinated drinks
- After COVID-19
23) Is JointOK+ safe? Does it have side effects?
Side effects are uncommon.
JointOK+ has no allergens, no sugar and no fats.
24) When to take JointOK+?
JointOK+should be taken with or after meals.
25) How long should I take JointOK+?
Take 1 pack JointOK+ (11.7 grams) daily until the bone mass density is ideal, generally 3 months to 1 year.
26) How to take JointOK+?
One sachet (containing 10g proprietary tendon-collagen peptide + 500mg calcium + 500 IU vitamin D + 75mg magnesium) after meal daily, serve by dissolving in room temperature or warm water
27) Where is JointOK+ produced?
JointOK+ is made in Germany.
28) Living with osteoporosis
To reduce chances of a fall, removing hazards in living and working places, correct eyesight and wear hearing aids if necessary.
29) Any Contraindications or Special Precautions?
Hypersensitivity, renal impairment, concurrent thyroid or antibiotic therapy due to drug interactions. Ask your doctor before use
| General | |
| Made In | Germany |
| Food | |
| Best Before Date | 1 Aug 2024 |
Write a review
Your Name:Your Review: Note: HTML is not translated!
Rating: Bad Good



































